Primo Research Assistant (Primo RA) is an AI-powered academic search tool integrated with PowerSearch to enhance literature discovery. Simply type in your questions in natural language, and the system will return 5 suggested sources and a summary.
Like all AI tools, Primo RA has both strengths and limitations. This guide aims to help you better understand the tool so you can use it more effectively in your research process:
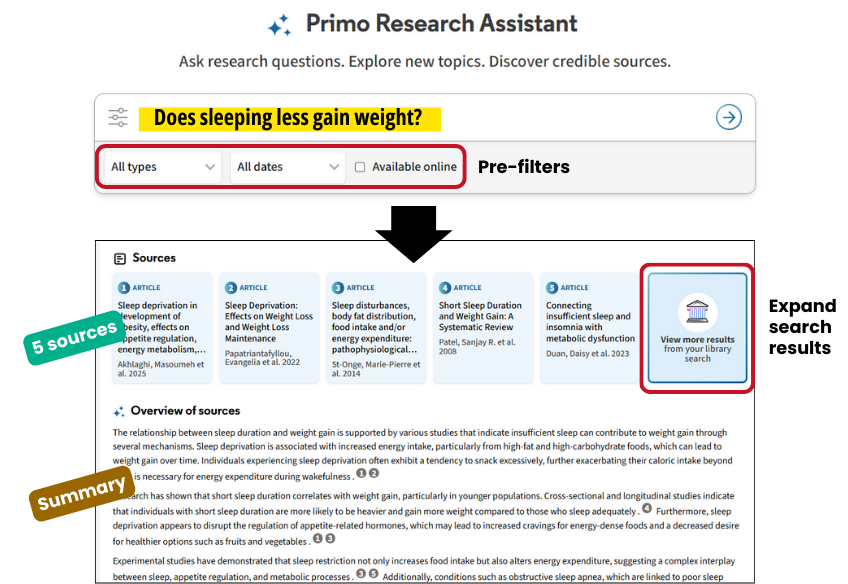
Use pre-filters to make your search more specific. E.g. type (peer-reviewed) and date (last 5 years).
When user inputs a natural language query, the LLM within Primo RA will convert it into a Boolean search query which typically contains keyword-based variations of original query, connected with “OR” operators.
The Boolean query is sent to Central Discovery Index (CDI), a giant database that contains over 5 billion scholarly material records, to retrieve the results. Note that this step is Keyword search (similar to directly typing keywords into PowerSearch) rather than Semantic search.
The top results (up to 30) are re-ranked using embeddings to optimize the relevance matching, and identify 5 sources that best address the user's query.
The top 5 results and their abstracts are sent to the LLM with the instructions to create the summary ("Overview") with in-text citations. The summary and sources are then shown to the user in the response.
2025.08 Primo Research Assistant - How It Works by Aster Zhao
|
👍 Pros |
👎 Cons / Limitations |
|
|---|---|---|
| Content Coverage |
|
|
| Search Capability |
|
|
| Quality of Generated Summary | - |
|