A journal is a publication released periodically which contains articles written by various authors.
Journal metrics provide a rating or ranking of a journal's overall contents, which can be compared with other journals.
Metrics measuring journal impact include:
Journal Impact Factor (JIF) is defined as all citations to the journal in the current JCR year to items published in the previous two years, divided by the total number of scholarly items (these comprise articles, reviews, and proceedings papers) published in the journal in the previous two years.
Calculation of 2015 impact factor of a journal:
A = the number of times articles published in 2013 and 2014 were cited by indexed journals during 2015.
B = the total number of "citable items" published in 2013 and 2014.
A/B = 2015 impact factor
Example 1: Find journal impact factor in InCites Journal Citation Reports

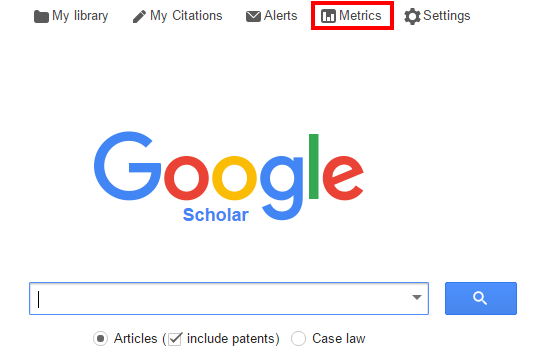
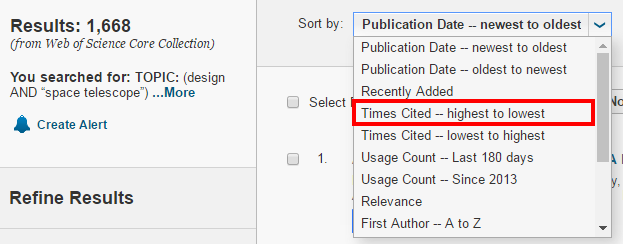
Example 2: Find journal impact factor in Web of Science




Other Metrics Available in InCites Journal Citation Reports
Article Influence Score:

Scopus can also be used to obtain metrics about the quality and importance of individual journals. The metrics that are calculated are the SCImago Journal Rankings (SJR), Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP) and CiteScore.
Calculation of SJR and SNIP of a journal:
https://youtu.be/5YarFhyoqeA
Calculation of CiteScore of a journal:
The calculation of CiteScore for the current year is based on the number of citations received by a journal in that year for the documents published in the journal in the past three years, divided by the documents indexed in Scopus published in those three years.
A = number of citations received by journal J in 2015 for documents published in 2012-14
B = documents published in 2012-14
A/B = CiteScore of journal J in 2015
CiteScore is calculated on an annual basis, showing the average citations for a full calendar year. CiteScore Tracker calculation is updated every month, giving a current indication of a journal's performance.
Major difference between CiteScore and Journal Impact Factor.
Example 1: Find SJR, SNIP and CiteScore in Scopus (Documents Search)



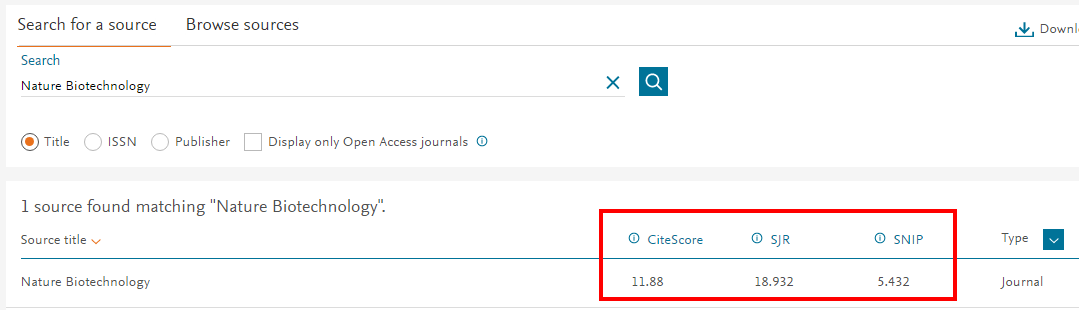
Example 2: Find SJR, SNIP and CiteScore in Scopus (Search for a Source)
Google Scholar Metrics include a top 100 list of journals for broad subject area, such as Business, Economics & Management, Engineering & Computer Science, and Humanities, Literature & Arts. Journals are ranked by h5-index and h5-median.
Example: Find h5-index and h5-median of a Journal in Google Scholar